When travelling in Belgium, any child under 1.35m in height must be transported in a suitable seat. In some neighbouring countries, the limit is set at 1.50m. Here are the different types of car seats available and their categories.
There are two authorised standards, R44/04 and iSize. The latter, which came into force in 2013, is becoming the standard to be used. R44/04 has categories based on weight, while iSize works with on the basis of the height of the child and includes Isofix fastenings as standard. Always choose a seat that has Isofix fittings so that you can properly secure the seat to the anchorage points that in turn secure it to the car. These anchorage points first appeared in 1995 and became widespread in 2003.

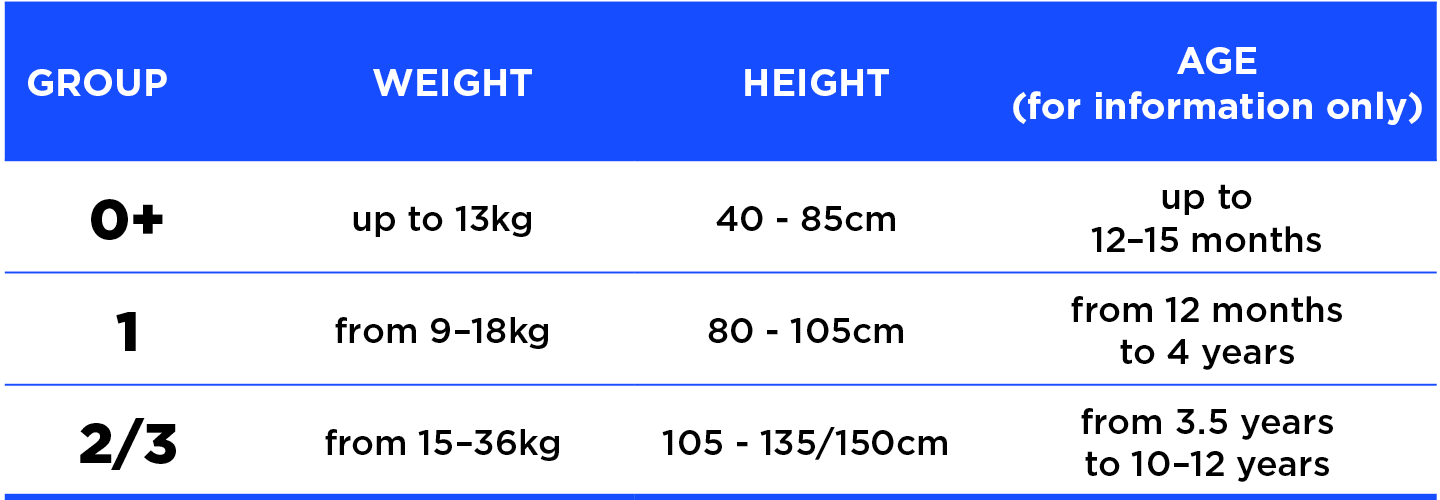
Groups
The different car seats are divided into groups, depending on the size of the child. Newborns under 15 months of age and children that are shorter than 85cm must be in a seat that is rear-facing. Your child can still travel in the front passenger seat in Belgium (this is not necessarily the case in other countries), but they can only be transported in a suitable seat. You should keep in mind, however, that the back seats are the safest. Warning: when you put your child in the front passenger seat with their back to the road, don’t forget to deactivate the airbag (either manually or automatically, depending on your model of car). This table shows the recommended group classification (avoid seats in group 1/2/3).
Which one should you choose?
First of all, you need to think about your child’s safety by choosing a new seat or one that has seen very little use (and most importantly, never use one that has been involved in an accident). It must be adapted to the size of the child, with side protection for the head and pelvis. The quality of the non-slip fabric, straps and padding is very important for your child’s comfort. The seat should not be too heavy and it should be easy to fix into the car. It will take some practice at first. Avoid any extra components or objects that could turn into projectiles in the event of an impact.
A newborn child under 85cm should be placed in a suitable rear-facing seat, the shell of which can also be used as a carry-cot and can even be attached to wheels so that it can be turned into a pushchair. Once the baby has grown above this limit, they can be placed in a group 1 seat (see below). In any case, this must happen as soon as your child’s head reaches above the shell.
Once your baby reaches the age of 15 months or is 85cm, their neck will be able to support the weight of their own head when the car brakes. At this point, your child can then be transported in a group 1 forward-facing seat that has straps integrated into the car seat structure. When your child reaches the height of 105cm, they will be able to use a group 2/3 seat. With these, your child will be held in place by the car’s seatbelt, guided by the car seat device.
The child can sit on a simple booster seat once they are 110cm or taller, but a seat with a backrest is recommended for children until they are 135cm tall. Although legally speaking, a child who is 135cm tall can simply travel in a car in Belgium using a seat belt – just as an adult would – booster seats are recommended until the child is 150cm tall. In some countries, such as Germany and Austria for example, a child must use a car seat until they reach a height of 150cm!






